Invisible digital pathways reveal how Wi-Fi has evolved into the high-speed backbone of modern connectivity.
Have you ever looked at a new router box and wondered why the Wi-Fi standard is now labeled with a 6 or a 7, instead of a simple number? If you’ve been trying to figure out what are Wi-Fi versions and what they mean, you are not alone.
It’s the invisible highway that transports our digital lives, letting us roam freely while staying connected. But to fully utilize this technology, it’s important to understand why they keep changing. Let me break down the evolution from Wi-Fi 4 to the cutting-edge Wi-Fi 7.
At its core, Wi-Fi, short for “Wireless Fidelity,” is simple: it lets your electronic devices connect to the internet using radio waves. Think of your Wi-Fi router as a miniature radio station and your devices like tiny radios tuned into that station.
Instead of broadcasting music, this station broadcasts data, converting it into radio signals that your devices can pick up and convert back into information.
When you send an email or stream a video, your device does the reverse, sending its own radio signals back to the router, which then forwards them to the internet. This two-way radio conversation happens incredibly fast, all without a single cable connecting your device to the network.
The magic of Wi-Fi is how it manages these signals.
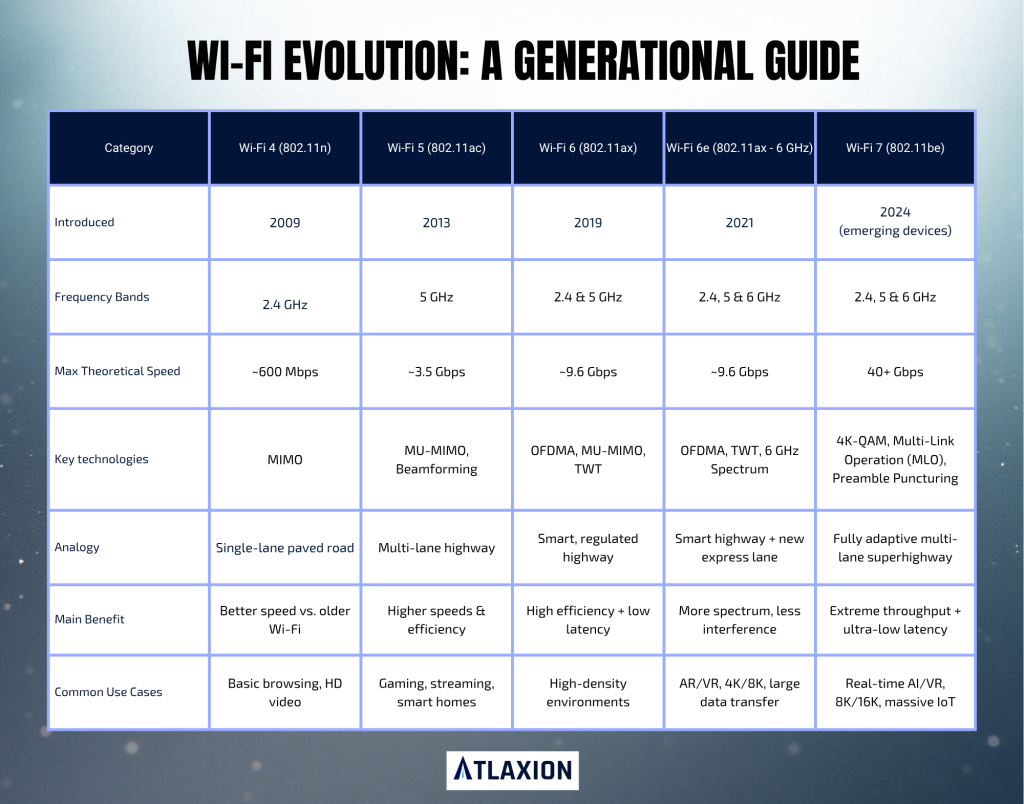
Different “flavors” of Wi-Fi, designated by numbers like 4, 5, 6, and now 7, represent significant upgrades in how efficiently and quickly this invisible communication happens. To truly grasp what are Wi-Fi versions, think of these numbers as progressively better traffic management systems for our invisible highway.
Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n): The First Paved Road
Introduced around 2007, Wi-Fi 4 was a game-changer. It was like finally paving the dirt road, allowing traffic to move much faster and more reliably. Before this, Wi-Fi was slow and prone to congestion. Wi-Fi 4 introduced MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) technology.
Imagine a single car trying to carry all your groceries. MIMO is like having multiple cars simultaneously, each carrying a portion of the groceries. This makes the entire delivery much quicker and allows for faster data transfer and improved range.
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac): Adding More Lanes
Arriving in 2013, Wi-Fi 5 was like adding more lanes to our paved highway. It primarily operated on the 5 GHz frequency band, which is less congested than the 2.4 GHz band used by older Wi-Fi versions and many other household devices.
Think of the 2.4 GHz band as a busy main street and 5 GHz as a quieter, higher-speed avenue.
Wi-Fi 5 also brought beamforming, which is like a smart headlight that focuses its light directly on your device rather than just broadcasting it everywhere, making for a stronger, more targeted signal.
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax): The Smart Traffic Controller
Launched in 2019, Wi-Fi 6 isn’t just about raw speed. It’s about efficiency, especially in crowded environments. Imagine our multi-lane highway, but now with a sophisticated traffic control system that knows exactly which cars need to go where and when.
Wi-Fi 6 introduced OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access), which is like allowing multiple smaller vehicles to share a single lane at the same time, significantly improving efficiency when many devices are connected.
The “e” in Wi-Fi 6E simply means it extends into a new, even wider and less congested 6 GHz frequency band, like opening up an entirely new, unbuilt section of the highway.
Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be): The Hyperloop of Data
Still relatively new and emerging, Wi-Fi 7, also known as “Extremely High Throughput” (EHT), is the next leap. If Wi-Fi 6 was a smart traffic controller, Wi-Fi 7 is like building a hyperloop for data.
It aims for even faster speeds and lower latency, which is crucial for things like advanced virtual and augmented reality. It achieves this by combining all three frequency bands (2.4, 5, and 6 GHz) more intelligently and employing even wider channels.
This essentially creates super-wide lanes for data to flow. If you want to know what are Wi-Fi versions capable of, Wi-Fi 7 represents the bleeding edge.
Final Thoughts
The impact of Wi-Fi’s continuous evolution is profound. It’s not just about faster downloads; it underpins the entire ecosystem of smart homes, remote work, online education, and entertainment.
From ensuring your smart speaker responds instantly to allowing doctors to perform remote consultations, Wi-Fi’s relentless improvement has quietly shaped our modern digital existence.
As our reliance on connected devices grows, the unseen force of Wi-Fi continues to build faster, smarter, and more robust invisible highways, ensuring our digital world remains seamless and accessible.